Empiricism
You may have heard the term “empirically determined.” This means something has been established based on practice. The expression “trial and error” is similar because you try something and see if it works or not. In Empirical working, we learn from practice, and this forms the basis for Scrum. However, we want to work in a structured manner, not just try everything. To do this, according to the Scrum framework, we need the other 3 pillars, as well as the foundation of trust.
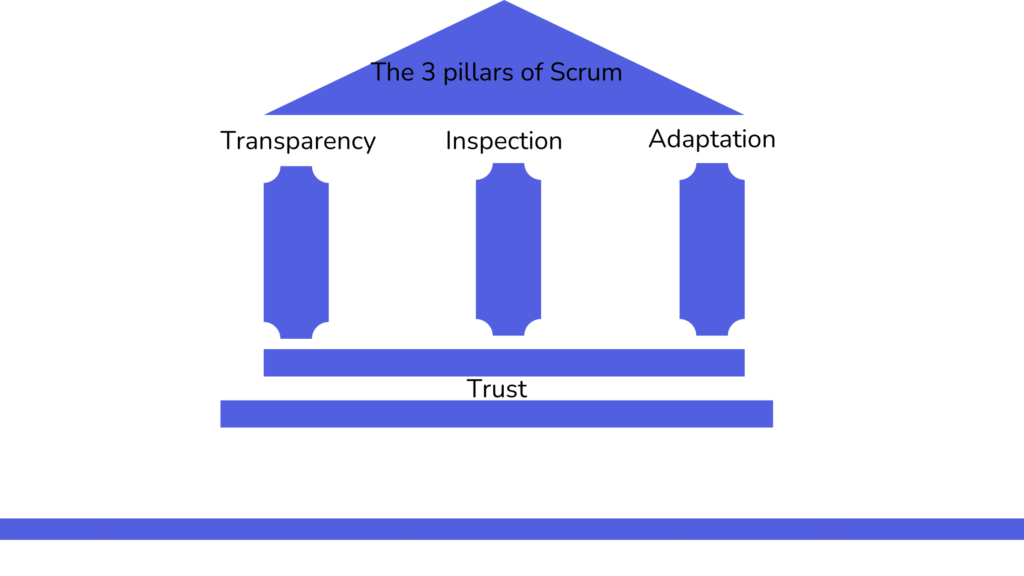
Trust
As mentioned earlier, the foundation for the pillars in Scrum is trust. Trust makes it possible to have the other pillars. For example, transparency is not possible without trust. Why would someone be transparent if the organization doesn’t trust them to make mistakes? A mutual trust between team members and the organization is crucial in Scrum, as it enables empirical working.
Transparency
Transparency is one of the core principles and 3 pillars within Scrum, ensuring that all aspects of the process are visible to everyone. This includes the work being done, the progress being made, and any obstacles that may arise. Through transparency, Scrum teams can make informed decisions, adapt to changes, and continuously improve. Key elements such as the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Burndown charts are made visible to everyone, allowing for clear communication and shared understanding. Transparency fosters trust among team members, stakeholders, and ensures alignment on goals, priorities, and expectations, contributing to successful outcomes.
Inspection
Inspection is an essential element and part of the 3 pillars within Scrum, where teams regularly assess progress toward goals and the quality of work. This process ensures that the team identifies problems, obstacles, or deviations early, allowing for timely adjustments. Scrum events such as the Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective promote continuous inspection of work and processes. Inspection is closely related to transparency, as it depends on clear, visible information about progress, challenges, and results. By inspecting regularly, the team can maintain an accurate view of the situation and make informed decisions to stay aligned with project goals—this is not possible without transparency.
Adaptation
Adaptation in Scrum refers to the team’s ability to adjust their approach based on insights gained through regular inspection. When the team identifies problems, inefficiencies, or changes in priorities, they adjust their plan, processes, or goals to stay on track. This flexibility ensures continuous improvement and alignment with project objectives. Adaptation is closely linked to transparency, as it relies on clear, accessible data about progress and challenges. When information is transparent, the team can make informed adjustments quickly, enabling them to respond effectively to emerging needs and remain aligned with both stakeholders and the broader vision.
Conclusion
The three pillars of Scrum—transparency, inspection, and adaptation—work together to create a framework that promotes continuous improvement and ensures teams can respond effectively to challenges. Transparency provides clarity and shared understanding, inspection allows teams to assess progress, and adaptation enables necessary changes to stay on track. When these pillars are embraced, Scrum teams are empowered to deliver high-quality results, adapt to changes, and achieve greater success in their projects.